Australian ILS Industry Support
Australia has a number of well qualified companies able to provide assistance to Manufacturers and Suppliers who have contracted to supply equipment to the Australian Defence Organisation (ADO)- Army, Navy, Air Force.
The support data and documentation required with the supplies is often under-estimated, and many Manufacturers and Suppliers of commercial equipment lack the experienced personnel to create the data or documentation in the appropriate format, which is where local contractors or consultants have their place.
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with :
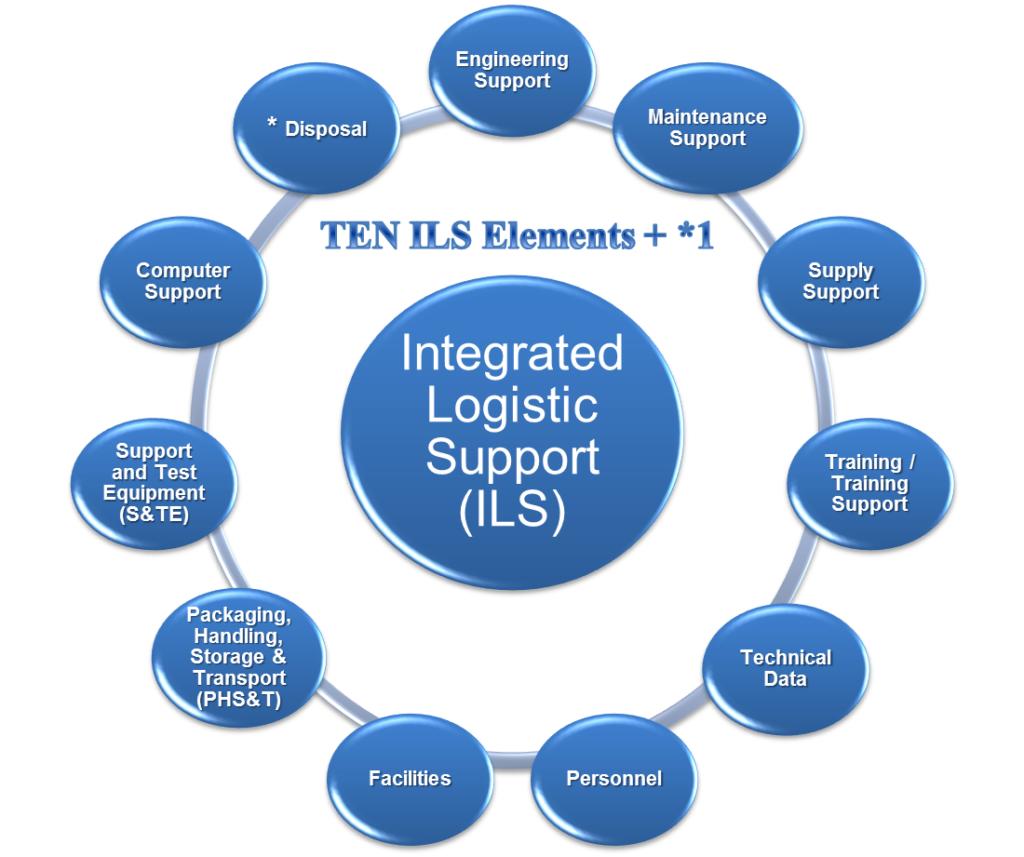
Defence contract Integrated Logistics Support Deliverables:
- Engineering Analysis for Maintenance Requirements
- Maintenance Engineering Analysis (MEA) / Maintenance Requirements Determination (MRD) for new and existing capital equipment;
- Failure Modes Effects Analysis (FMEA);
- Failure Modes, Effects and Criticality Analysis (FMECA);
- Reliability Centred Maintenance (RCM);
- Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA); and
- Investigation and validation of Engineering Change Proposals.
- Supply Support
- Sparing Analysis inclusive of Recommended Provisioning Lists (RPL) / Manufacturers Recommended Parts Lists (MRSL);
- Codification Data (CDATA) Packs;
- Complete Equipment Schedule Lists (CESL);
- Training Equipment Management List (TEML);
- Australian Defence Aviation Authorised Spares Sets (ADAASS); and
- Packaging, Handling, Storage and Transportation (PHS&T).
- Technical Authoring
- Development of management plans;
- Repair and Maintenance manuals and illustrated parts manuals;
- Development of Australian Defence specific documentation and manuals such as:
- Electrical and Mechanical Engineering Instructions (EMEIs);
- User Handbooks (UHBs);
- Australian Book of Reference (ABR), and Australian Air Publications (AAP);
- Parts, system and repair manuals; and
- Repair Parts Identification Lists (RPILs) and associated Repair Parts Scales (RPSs);
- Company Operating Procedures and Standing Instructions; and
- Investigation of maintenance and repair requirements and to document the maintenance requirements of an item or equipment throughout its service life.
- Training Development and Delivery
- Conduct of Training Needs Analysis;
- Development of Training Recommendation Reports;
- Development of Training Management Plans;
- Development of Training Materials; and
- Delivery of Training courses.
- Tendering and Bid Support
- Review and enhance tender submissions.
- Develop and author management, quality and the range of ILS plans /sub-program plans as part of major tender submissions for prime Defence contractors and Small to Medium Enterprises (SME) and commercial industry tendering to government projects; and
- Review and provide advice on tender structure and content for Defence and commercial industry;
- Project Support Services
- Develop or Review ILS plans and reports;
- Maintenance Program Optimisation;
- Configuration Management;
- Database Administration; and
- Independent Audits.
LES capabilities and Experience
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with:
Defence contract Integrated Logistics Support Training
Logistic Engineering Services – ILS Training
- ILS Executive Overview;
- ILS Practitioner Training;
- Logistic Support Analysis Record (LSAR) Training;
- Level of Repair Analysis (LORA) Training; and
- Maintenance Requirements Determination (MRD) Training.
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with:
Defence contract Maintenance Requirements Determination (MRD) software :
Logistic Engineering Services eMRD
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with
Defence contract LSAR comparison software :
Logistic Engineering Services eMRDCompanion
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with
Defence contract Logistic Support Analysis Records (LSAR) software:
Logistic Engineering Services eLSA
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with
Defence contract Level of Repair Analysis (LORA) software:
Logistic Engineering Services eLORA
ILS Software Users and Projects
Australian ILS Industry Support companies available to assist suppliers with
Defence contract Australian Local Content:
Defence contract Project Management Support